How Does Health Insurance Works in India? A Complete Guide
In India, a layman’s knowledge of health insurance is only as good as what they read or see in an advertisement or what they heard from friends and family. Those who do have health insurance policies might know better than those who do not have a policy.
Understanding how health insurance works are not that difficult. All you need to do is, first get the basics right and then get into the details. Let’s dissect the different parts of health insurance to understand it better.
What is Health Insurance?
Health insurance is an agreement between an insurance company and a customer. An insurance policy provides financial protection against medical treatments, hospitalization, diagnostic costs, and other healthcare demands. In short, it provides financial coverage towards the healthcare expenses of the policyholder – the insured.
How does Health Insurance Work in India?
Different health insurance plans may follow different processes and regulations. Typically, this is how health insurance works in India:
There are many insurance companies in India. Most insurance companies offer different kinds of insurance – health, life, auto, home, accident, theft, business-related insurance and more.
Health insurance companies offer different kinds of plans that cater to different needs, age groups and illnesses. Customers can choose a plan that suits their needs. Anyone can have more than one health policy.
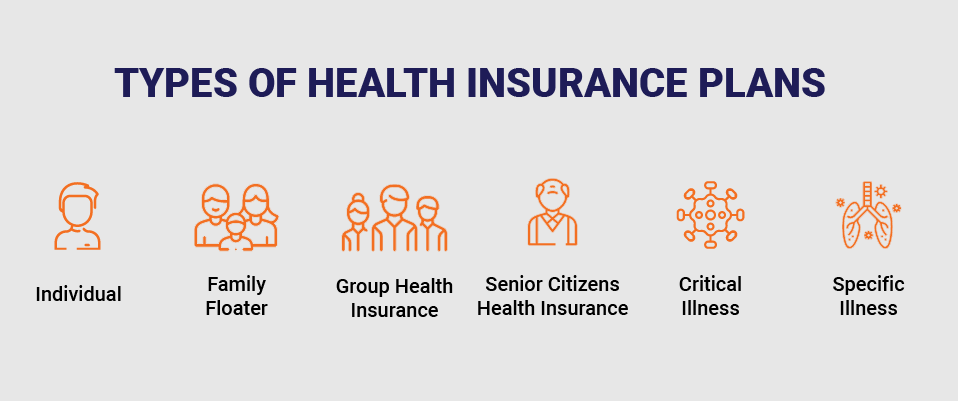
Types of Health Insurance Policies in India
The broad categories and the most popular types of health insurance are mentioned below:
- Individual Health Insurance: plans for a single individual, where the entire sum insured is applicable to only the individual insured.
- Family floater Insurance: plans that provide coverage to all the family members who are part of the policy. Here, the sum insured can be utilized by one, any, or all the members in part or full.
- Group Health Insurance: employers and corporate companies provide health insurance to their employees. Such insurance plans are mostly group health insurance, under which, several individuals are insured under a single plan.
- Senior Citizen Health Insurance: These plans are specially designed for senior citizens aged 65 years and above. Health plans for senior citizens usually come at a higher premium because of the higher health risk probability among older people.
- Critical Illness Insurance: certain health insurance plans are specifically designed to cover the costs towards critical or chronic diseases only. These diseases are diabetes, cancer, cardiac and cardiovascular ailments, hypertension and other related ailments.
- Disease-Specific Illness Insurance: these plans are designed to provide coverage only for the diseases specified in the plan, e.g. COVID-specific insurance plan, maternity-specific insurance, heart-specific health plan, among others.
- Bite-size Health Insurance plans: Quite recently, many insurance companies introduced smaller health insurance plans with bite-size premiums to cover seasonal diseases such as dengue, vector-borne diseases among others.
- Top-Up and Super Top-Up Health Insurance Plan: A top-up insurance plan is a regular plan that offers hospitalization coverage but when a limit is crossed. This limit is known as the deductible. A deductible is the amount of sum insured that is the policyholder’s responsibility. The insurer does not cover it.
Check out this cool infographic that also explains the basics of health insurance.
The process of buying health insurance
Buying a health insurance plan is easier said than done. These are some essential steps to ensuring you buy a health plan that meets your and your family’s needs.
Determine your healthcare needs: health insurance is an investment, but it could turn into an expense if not purchased with care. It is therefore important to first assess your and your family members healthcare needs. Consider these factors:
- Young couples must consider family planning and maternity health insurance
- Those who have a large family must assess the healthcare needs of each family member – elderly parents, young children, siblings and senior grandparents. This will help you decide whether personal plans for different members or a family floater would be more suitable for you.
Calculate the amount of sum insured requirement: take into consideration the current healthcare expenses, the future probable and sudden accidental expenses. Don’t forget to factor in inflation. In India, medical inflation accounts for the highest share of overall inflation.
Compare health insurance plans and insurance companies: once you have a clear picture of your requirements, select a few plans from different health insurance companies, and power up your personal finance goals. Compare different plans. Look for these differences and identify benefits:
- Premium
- Add-on offered
- Pre and post hospitalization coverage range
- Illnesses and diseases covered
- Flexibility – portability option, possibility of adding a new member, increasing or decreasing sum insured.
- Claim settlement ratio of the company
- The insurance company’s performance history and reviews
- Network hospitals
- Cashless claim facility
- Waiting period for pre-existing diseases
- Pre-existing diseases clauses
- Exclusions
- Co-payment and sub-limit clauses
Share complete and correct information: Once you’ve zeroed in on an insurance plan, disclose all the required details completely and correctly. Any discrepancies may result in rejection of the policy or claims at the time of hospitalization or medical emergencies.
How much does health insurance cost in general?
There are many factors that determine the cost of a health insurance plan. The cost of a health insurance plan depends on the individual’s needs and conditions. Different people pay different premiums. The most basic factors that contribute to the price of health insurance premiums are:
- The age of the insured. The older a person, the more the price of the premium. In the case of a family floater, the age of the oldest member determines the premium.
- The lifestyle and current health conditions
- Pre-existing diseases and critical illnesses
- The occupation and income
- The type of plan, the coverage offered, etc.
What is the claim process for health insurance?
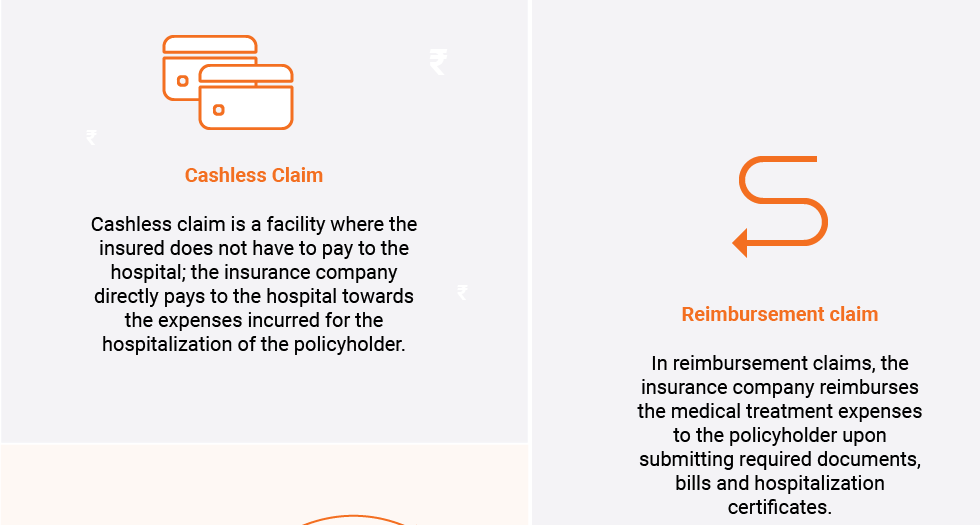
The claim process is nothing but the request from a policyholder to the insurance company to compensate/make payment for the medical treatment costs incurred by the policyholder. There are two types of claims:
- Cashless Claim
- Reimbursement Claim
For both types of claims, health insurers follow a set of processes, which has to be completed within a few days to a few weeks of the hospitalization. Typically, the process involves informing the insurance company about the medical procedure/emergency within a specified time frame, submitting a claims form and the required documents. The insurance company then investigates the documents to release the payment.
1. Cashless Claim
Cashless claim is an agreement between the insurer and the network hospitals to allow policyholders treatments without any payments from the policyholder. In this type of claim, the insurer pays directly to the hospital. The policyholder does not have to make the payment and then receive it back as reimbursement from the insurance company.
This process, typically, follows these steps:
- Get treatment at a hospital part of the network of the insurance policy
- Submit a health insurance policy claim form at the hospital
- The insurance company sends an approval to the hospital or raises a query in case of missing information
2. Reimbursement Claim
In this type of claim, the policyholder has to make the payment to the hospital, which is then reimbursed by the insurer upon following the reimbursement process, as follows:
- The policyholder is required to fill out a claims form and submit it to the insurer along with the medical and hospital bills
- The insurer then investigates the documents
- If the claim is approved, the insurance company sends an approval letter. In case of rejection, a rejection letter along with the reasons is shared with the policyholder.
To see more such insurance terms, visit this infographic.
Tax Saving with Health Insurance
Policyholders can avail of tax benefits on the premium paid, under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act. Policyholders can avail of as much as Rs 1 lakh tax deductions on health insurance plans.
Income Tax Deductions Bcreak-up under Section 80D
| Age groups | Self, spouse, children | Senior citizens | Total tax deductible (upto) |
| Policyholder under 60 years | 25,000 | – | 25,000 |
| Policyholder under 60 years | 25,000 | 25,000 | 50,000 |
| If the eldest member in the family is under 60 years and parents are over 60 years | 25,000 | 50,000 | 75,000 |
| If the eldest member in the family is over 60 years and the parents are also over 60 years | 50,000 | 50,000 | 1,00,000 |
Learned the basics of health insurance? Know how health insurance works? Well done! To understand more about health insurance or to purchase a plan, get in touch with our representatives.
FAQs: Health Insurance Basics
Is there a minimum and maximum age for buying health insurance?
Most health insurance companies in India have an age bracket for entry and exit and maximum buying age. However, this depends on the type of health insurance plan. From a one-day old baby to a teenager to a senior citizen aged 90, anyone can have a health insurance plan.
How much health insurance sum insured is ideal?
The sum insured requirements for different people are different, depending on the age, health conditions, and medical history of the policyholder. It is not a rule of thumb, but experts suggest that most urban dwellers should have a sum insured of at least Rs 3 lakh to 5 lakh. With healthcare costs rising steeply, year-after-year, it is advisable to have a bigger sum insured of up to 10 lakhs or 20 lakhs.
What is health insurance?
Health insurance is a kind of transaction or agreement between the health insurance company and the policyholder. The policyholder pays an annual premium to the insurance company in return of financial security against healthcare, medical and hospitalization needs. In case of medical emergencies and hospitalization, the insurer provides financial coverage to the policyholder.